Total Hardness Photometer
The Urgency of Water Testing in Industrial Production
Have you ever realized that hard water could be silently causing severe damage to your production equipment and lowering product quality without being easily detected? Testing for water hardness not only protects machinery and reduces maintenance costs, but also ensures smooth operation of the production process. Let’s explore the most effective methods of measuring water hardness that could become a lifesaver for your business!
Is Water Testing in Industrial Production Necessary?
Water is an essential component in almost all industrial production processes, from cooling, washing, mixing, to chemical manufacturing, food, pharmaceuticals, and many other industries. Water quality directly affects operational efficiency, equipment lifespan, product quality, and even operational costs.
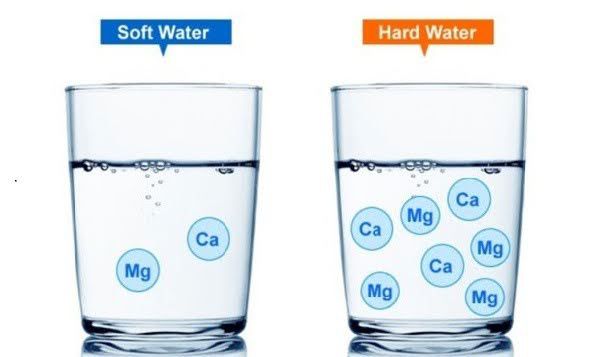
Periodic water testing helps detect early signs of water quality issues such as hardness, pH level, heavy metals, microorganisms, etc., enabling timely solutions to ensure uninterrupted production and product quality compliance.
- Risks of Not Testing Water Properly
If water hardness and other quality parameters are not properly tested, water may contain harmful impurities such as calcium, magnesium, iron, chlorine, bacteria, etc. These elements can cause:
Blockages and equipment corrosion: Especially in piping systems, boilers, and cooling systems, leading to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs.
Product quality degradation: Substandard water can affect taste, color, and safety of products in food and pharmaceutical industries.
Health risks: Contaminated water can affect the health of workers and consumers.
Legal violations: Failure to meet water quality standards can result in administrative fines or production suspension.
Water Hardness Testing - A Crucial Step in Water Quality Control
Among water quality indicators, water hardness testing is one of the most critical steps. Hard water contains high levels of calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions, leading to scaling, reduced equipment efficiency, and increased operational costs.
Measuring water hardness allows businesses to accurately assess the impact of hard water and choose appropriate treatment methods such as water softening or anti-scaling chemicals.
Water Hardness Measurement and the Impact of Hard Water in Industry
Definition and Significance of Water Hardness Measurement
Water hardness refers to the concentration of dissolved calcium and magnesium ions in water, measured in units such as mg/L CaCO3, dH, F, or grains per gallon (gpg). Measuring water hardness determines how "hard" the water is and evaluates its potential to cause scaling and corrosion.
Negative Effects of Hard Water in Industrial Production
Scaling and reduced equipment efficiency: When hard water is heated or evaporates, calcium and magnesium ions precipitate and form scale on surfaces like boilers, pipes, and pumps, reducing heat transfer and water flow.

Increased maintenance costs: Scale buildup leads to damage, shortened equipment lifespan, and higher repair or replacement expenses.
Higher energy consumption: Reduced efficiency forces machinery to consume more energy to achieve desired performance.
Impact on product quality: In the food industry, hard water can alter flavor, color, and hygiene.
Environmental issues: Improper treatment of hard water can generate large volumes of waste and impact the surrounding environment.
The Importance of Periodic Water Hardness Testing
Regular water hardness testing helps to:
Detect changes in water quality early for timely treatment.
Protect equipment from scale-related damage, extending machine lifespan.
Optimize production processes and reduce operating costs.
Ensure final products meet quality and safety standards.
Comply with environmental and occupational safety regulations.
Common Methods of Water Hardness Testing and Real-World Applications
1. Traditional Water Hardness Testing Methods
Titration method: Uses EDTA solution to react with calcium and magnesium ions in water samples. This is an accurate and widely used method in laboratories.
Test strips: Dip strips into water samples; color changes indicate hardness level. Quick and convenient but less accurate than titration.
Soap test: Uses soap to test lathering ability; hard water reduces lather. Simple, qualitative method.
2. Modern Water Hardness Testing Methods
Electronic water hardness testers: Devices use electrochemical or optical sensors to directly measure hardness, providing fast, accurate results with data storage capabilities.
Bluetooth-enabled testers: Modern devices like the Hinotek S40 connect wirelessly to smartphones for easy tracking and result management.
3. Applications of Water Hardness Testing in Industry
Food and beverage manufacturing: Ensures production water does not affect product flavor and quality.
Pharmaceutical industry: Ensures water meets cleanliness standards and does not impact active ingredients.
Power generation: Tests cooling water and boiler water to prevent scaling and corrosion.
Chemical and metallurgy industries: Controls water quality for stable and safe production processes.
See details at: What is water hardness? What are the methods of measuring water hardness?
Conclusion
Water hardness testing in industrial production is a vital step to protect equipment, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure product quality. Measuring water hardness helps detect and promptly address issues caused by hard water, thereby minimizing costs and production risks.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
